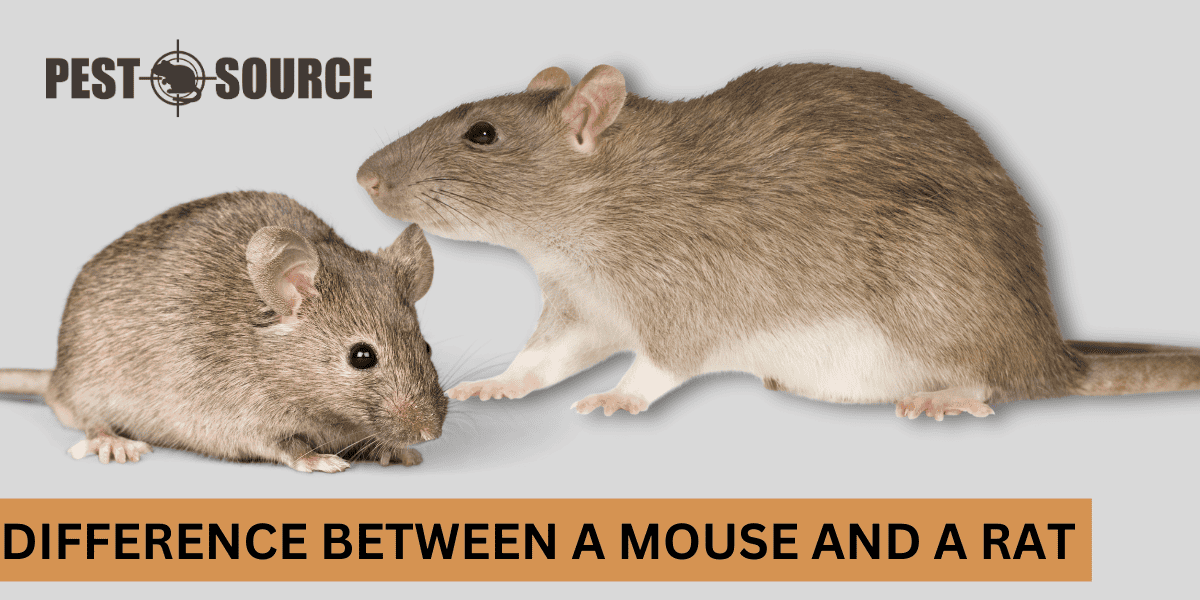
Understanding the difference between a mouse and a rat is crucial for effective pest control. While they may seem similar at first glance, there are distinctive physical and behavioral traits that set them apart. Proper identification is the first step in addressing any rodent problem. Let’s delve into the key differences between these two common pests.
POINTS
- Rats and mice have distinct physical characteristics such as size, fur texture, ear size, and tail length, with rats generally being larger and having coarser fur than mice.
- Behavioral differences are notable; rats live in hierarchical social structures and are more adaptable, while mice are less social and reproduce rapidly, making infestations difficult to eradicate.
- Both rodents pose significant health risks by carrying diseases and can cause structural damage, with rats capable of gnawing through wood and wires, and mice chewing on materials and nesting within walls.
- Effective pest control requires understanding the specific behaviors and signs of infestation for each species, as rats leave droppings and grease marks, while mice are more discreet until their population becomes significant.
- Rats and mice require different pest management strategies due to their differing social behaviors, communication methods, and adaptability, with rats learning to avoid dangers and mice exploiting small spaces.
Physical Differences Between Mice and Rats
Mice and rats differ significantly in appearance. Here are some of the most noticeable physical distinctions:
Size
- Mice: Typically smaller, with bodies that can be 2 to 4 inches in length.
- Rats: Larger, with bodies that can reach up to 9 to 11 inches long.
Fur Texture
- Mice: Their fur is usually soft and fine.
- Rats: They tend to have coarser fur.
Ear Size
- Mice: Have larger ears in proportion to their head.
- Rats: Their ears are smaller relative to their body size.
Tail Length
- Mice: Possess long, thin tails with some hair.
- Rats: Have thicker, hairless tails.
Behavioral Differences
The behavior of mice and rats can provide insights into their identification and control.
Nesting Habits
- Mice: Prefer to build nests in hidden areas using soft materials like fabric or paper.
- Rats: Often burrow underground or in secluded areas of buildings.
Social Structure
- Mice: Are typically more solitary.
- Rats: Have a more complex social structure, living in larger groups.
Typical Environments
- Mice: Adapt well to indoor environments and can often be found in homes.
- Rats: Tend to inhabit both indoor and outdoor areas, including sewers and fields.
Dietary Preferences
- Mice: Are omnivorous but prefer grains and seeds.
- Rats: Have a more varied diet and will eat almost anything available.
Genetic and Biological Distinctions
Mice and rats not only look different, but they also have distinct genetic and biological makeups.
Species Classification
- Mice: Belong to the genus Mus.
- Rats: Are part of the genus Rattus.
Evolutionary History
- Mice and rats have evolved differently, leading to the distinct species we recognize today.
Physical Characteristics and Genetic Distinctions
Going beyond the basics, let’s explore more about what sets these rodents apart.
Tail Length and Body Size
- Mice: Have longer tails in proportion to their body size.
- Rats: Their tails are shorter when compared to their larger body size.
Fur Color
- Mice: Commonly light brown or grey.
- Rats: Typically brown or grey, but can vary significantly.
Ear Size
- Mice: Their larger ears can be a key identifying feature.
- Rats: Smaller ears that do not stand out as much.
Genetic Differences
- Mice and rats have different chromosome counts, which contributes to their physical differences and species-specific traits.
Common Misconceptions
- Despite popular belief, mice and rats are not simply different sizes of the same species. They are distinct both genetically and behaviorally.
Rats and Mice in Human Environments: Interactions and Implications
When rats and mice enter human living spaces, they bring with them a host of challenges. Understanding how each species interacts with these environments is key to managing their populations and mitigating the risks they pose.
Pest Control and Public Health Concerns
Rats and mice are known for their ability to spread disease and cause structural damage, making them significant pests.
Disease Transmission
- Rats: Can carry a variety of diseases, such as leptospirosis and hantavirus.
- Mice: Also carriers of diseases, including salmonella and Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCMV).
Structural Damage
- Rats: Have strong teeth that can gnaw through wood, electrical wires, and even concrete.
- Mice: Cause damage by chewing on materials and building nests within walls.
Challenges in Population Management
Controlling the populations of rats and mice requires different approaches due to their varied behaviors.
Identifying Infestations
- Rats: Leave evidence of their presence through droppings, grease marks, and burrows.
- Mice: Smaller and more discreet, their infestations can be harder to detect until they’ve become significant.
Managing Infestations
- Rats: Often require professional extermination and environmental modifications to prevent re-entry.
- Mice: Can sometimes be managed with traps and sealing entry points, but may also require professional assistance.
Social Behavior and Communication: Comparative Analysis
The social structures and communication methods of rats and mice have implications for their control and prevention.
Rat Social Structures
Rats are social animals that live in hierarchical groups. They communicate through a variety of sounds and scents to establish social order, warn of danger, and coordinate activities. This social behavior can lead to large infestations that are challenging to control.
Mouse Communication
Mice, while less social than rats, still communicate with each other through high-pitched sounds and pheromones. They tend to have smaller territories and can live in close proximity to humans without immediate detection.
Impact on Survival and Adaptability
The social behaviors of rats and mice affect their ability to survive and adapt in various environments.
Rats
- Their social structure allows them to quickly learn from each other and avoid dangers, such as traps.
Mice
- They can reproduce rapidly and exploit small spaces, making them difficult to eradicate once they’ve settled in an area.
Interaction Within Their Species and Environments
Both rats and mice have evolved to thrive alongside humans, but their different social behaviors necessitate tailored approaches to pest control. By understanding these behaviors, pest control professionals can develop more effective strategies for managing rodent populations and preventing future infestations.
In summary, while rats and mice share some similarities, their differences are significant. From physical attributes to behavior and social interactions, these distinctions play a crucial role in identifying, controlling, and preventing these common pests. Whether dealing with a small mouse problem or a full-blown rat infestation, knowledge is power in the world of pest management.