Fleas are tiny parasites that pose significant challenges to pet owners, home dwellers, and in some cases, even health professionals. The speed and efficiency with which they reproduce play a central role in their invasiveness, causing infestations that can seem almost impossible to control.
This article will journey through the intriguing world of fleas, illuminating their lifecycle, exploring the rapidity of their reproduction, investigating their unique abilities and behaviors, and examining their interaction with hosts. Additionally, we will draw comparisons with other parasites and provide essential tips for managing infestations. By comprehending the nuances of flea biology, specifically focusing on how fast fleas reproduce, one can adopt more effective strategies for their prevention and control.
POINTS
- Fleas reproduce rapidly, with adult females laying up to 50 eggs per day and completing their entire lifecycle in as little as 14 to 28 days, leading to quick and severe infestations.
- Fleas are fast-moving and remarkable jumpers, making it easy for them to find and infest hosts, quickly spread, and travel between environments.
- Stopping the flea cycle requires a combination of pet flea treatments, regular home cleaning and vacuuming, and possibly professional extermination for stubborn infestations.
- Fleas can transmit diseases to humans and animals, highlighting the necessity of promptly addressing and managing infestations.
- Both indoor and outdoor environments should be treated to prevent reinfestation, and pets should be regularly checked and treated to maintain a flea-free home.
Understanding Flea Biology and Lifecycle
What Is The Lifecycle Of A Flea?
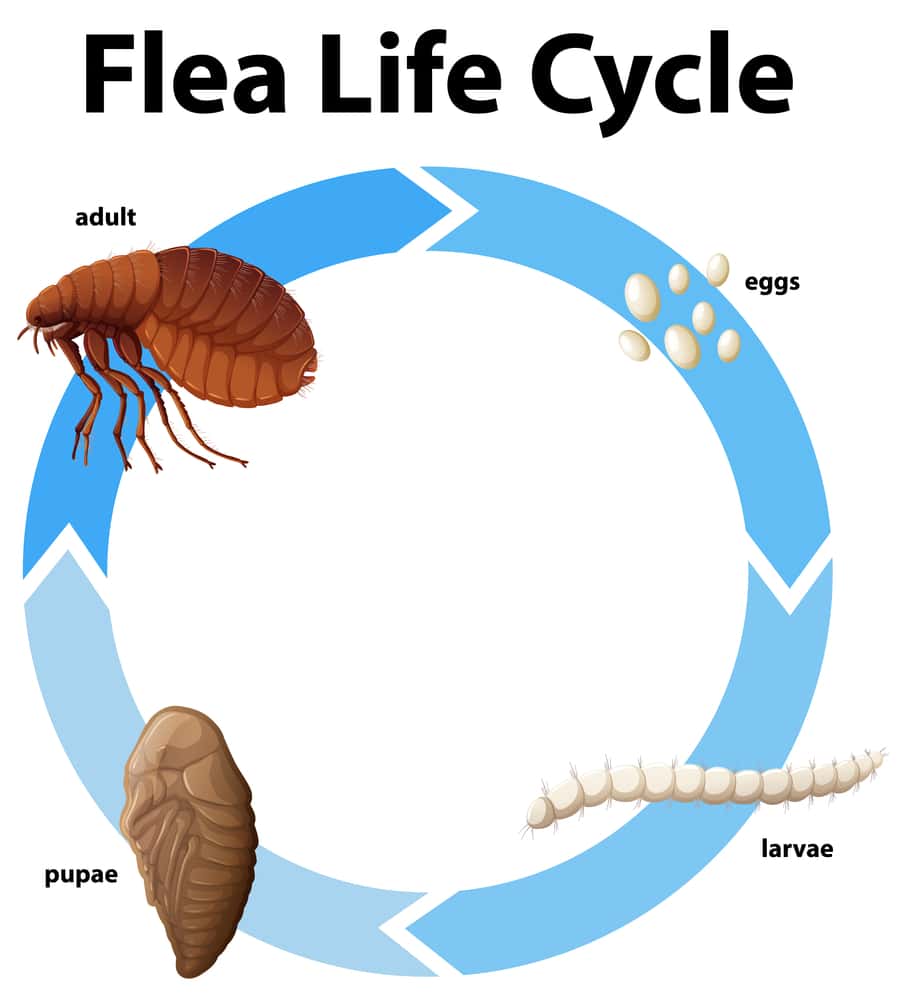
The lifecycle of a flea consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Understanding their lifecycle helps us grasp how rapidly they reproduce and how to effectively deal with infestations.
How Quickly Do Fleas Grow?
Fleas grow rapidly, often completing their entire lifecycle in as little as 14 to 28 days. Environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can impact their development time, with ideal conditions (70°F – 85°F and 50% to 90% humidity) leading to faster maturation.
What Are The Key Stages In The Flea Cycle?
Understanding the lifecycle of a flea is essential for effective flea management and control. The table below provides an overview of the four key stages of a flea’s lifecycle, including the duration of each stage, characteristics, and the environmental conditions that favor their development.
| Stage | Duration | Characteristics | Preferred Environmental Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg | 2-14 days | Laid by female fleas, often in clusters; found in pet fur or the environment | Warm, humid (50-90% humidity) |
| Larva | 5-20 days | Feeds on organic debris; avoids light; burrows into carpets, etc. | Dark, protected areas; warm, humid |
| Pupa | 4 days to several months | Larva spins a cocoon; highly resistant to insecticides | Protected environments; influenced by environmental conditions |
| Adult | Several weeks to several months | Begins to feed and reproduce upon finding a host; highly mobile | Close to host for feeding; capable of surviving in a wide range of conditions |
The Reproduction of Fleas
To effectively tackle flea infestations, it’s crucial to grasp how fleas reproduce, including their rapid rate of egg laying and the lifespan of adult fleas. The table below outlines key aspects of flea reproduction, providing insights into the volume of eggs laid, the timing of reproduction following a meal, and the overall potential for infestation.
| Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Eggs laid per day by an adult female | Up to 50 |
| Total eggs during an adult female’s lifespan | Up to 2,000 |
| Time to first egg-laying after first blood meal | Within 24-48 hours |
| Lifespan of an adult flea | Several weeks to several months |
How Do Fleas Reproduce?
Fleas reproduce through a process called holometabolic metamorphosis, in which they pass through the four distinct stages mentioned above. Mating typically occurs soon after the adult female and male fleas emerge from their cocoons, and the female flea begins laying eggs within 24 to 48 hours after her first meal.
How Quickly Do Fleas Multiply?
Fleas can multiply rapidly, with adult females laying up to 50 eggs per day and producing up to 2,000 eggs during their lifespan. This exponential growth can lead to large infestations in a short period, especially if conditions are favorable.
How Many Eggs Do Fleas Lay In A Day?
An adult female flea can lay up to 50 eggs per day, depending on factors such as host availability, environmental conditions, and flea species. Some flea species may lay fewer eggs, while others may lay more.
How Fast Do Fleas Breed?
Fleas breed quickly, with adult fleas typically mating soon after emerging from their cocoons. Once a female flea has had her first blood meal, she can begin laying eggs within 24 to 48 hours.
How Often Do Fleas Reproduce?
Female fleas can continuously lay eggs throughout their adult lives, producing more offspring as long as they have access to a blood meal. The exact frequency of reproduction depends on the flea species and environmental conditions.
How Long Does It Take For Fleas To Reproduce?
A flea can complete its lifecycle and reproduce within 14 to 28 days, depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and food availability. In ideal conditions, fleas can reproduce quickly and become a significant problem.
The Speed and Behavior of Fleas
Fleas are not only notorious for their ability to reproduce rapidly but also for their remarkable speed and agility, which contribute significantly to their infestation capabilities.
| Attribute | Detail |
|---|---|
| Speed | Up to 1.5 feet per second |
| Jumping height | Up to 7 inches (18 centimeters) |
| Jumping distance | Up to 13 inches (33 centimeters) |
| Movement method | Crawling and jumping, using legs and resilin pad for powerful jumps |
How Fast Are Fleas?
Fleas are fast-moving insects, capable of reaching speeds of up to 1.5 feet per second. Their size, agility, and ability to jump allow them to quickly locate and infest their hosts, often going unnoticed until they have multiplied into a larger population.
How Far And High Can Fleas Jump?
Fleas are impressive jumpers, thanks to their strong legs. They can jump vertically up to 7 inches (18 centimeters) high and horizontally up to 13 inches (33 centimeters). This incredible jumping ability allows them to easily hop onto hosts or traverse their environments in search of a meal.
How Does A Flea Travel So Fast?
Fleas are fast travelers due to their small size, legs specifically evolved for jumping, and streamlined bodies. They can cover large distances relative to their size by jumping and crawling through their environment, allowing them to quickly attach to potential hosts or seek out hiding spots.
How Do Fleas Travel?
Fleas travel both by crawling and jumping. They use their legs for crawling and leverage the resilin pad at the base of their hind legs for their powerful jumps. These jumps enable them to rapidly cover ground, jump onto hosts, and navigate their environments.
The Infestation and Spread of Fleas
How Fast Do Fleas Spread?
Fleas can spread quickly, mainly due to their rapid reproductive rate and efficient means of travel. The fleas’ ability to infest new hosts, lay up to 50 eggs per day, and quickly traverse their environments contributes to their rapid spreading.
How Fast Can Fleas Spread In A House?
The speed at which fleas spread within a house can vary, but it can happen rapidly if measures to control their growth are not taken. Factors such as the presence of pets, suitable hiding spots, and favorable environmental conditions all contribute to how quickly fleas can infest a home.

How Far Can Fleas Travel?
Fleas can travel long distances relative to their size through jumping and crawling. They can jump up to 13 inches (33 centimeters) horizontally, allowing them to quickly traverse their environment and find new hosts.
Can Fleas Spread From House To House?
Fleas can potentially spread from house to house, although it is not as common as spreading within a single home. This can happen when animals or people unknowingly transport fleas on their clothing, fur, or belongings from one location to another.
How To Stop Fleas From Spreading?
To stop fleas from spreading, it’s crucial to implement a comprehensive approach that targets the infestation from multiple angles. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Regular Cleaning and Vacuuming: Maintain cleanliness in your home by frequently vacuuming carpets, furniture, and floors to remove fleas, eggs, and larvae.
- Pet Flea Treatments: Use recommended flea treatments for your pets, such as topical applications or oral medications, to eliminate fleas on them.
- Wash Pet Bedding: Regularly wash your pet’s bedding in hot water to kill any fleas and prevent their eggs from hatching.
- Insecticides: For severe infestations, consider using insecticides in your home, following safety guidelines to protect your family and pets.
- Professional Exterminator: If the infestation persists, it may be necessary to work with a professional exterminator to effectively target and eliminate fleas.
Fleas and Their Interaction with Hosts
Understanding how fleas interact with their hosts is pivotal in managing and preventing infestations effectively. The table below provides a comparative overview of how fleas get on and affect different hosts, such as dogs, cats, and humans, highlighting the methods of transmission and potential impacts.
| Host Type | Method of Transmission | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dogs | Contact with infested environments/animals | Fleas feed on blood, causing irritation, allergic reactions |
| Cats | Contact with infested environments/animals or other infested cats | Similar to dogs, can cause severe discomfort and allergic responses |
| Humans | Fleas can jump from infested pets or environments | Typically result in bites and itching; less commonly, transmission of diseases |
How Do Fleas Get On Dogs?

Fleas typically get on dogs when the animal comes into contact with an infested environment, such as an outdoor area with fleas or another infested animal. Fleas will jump onto the dog when it is close enough, then begin feeding and reproducing.
Do Fleas Jump On Cats?

Yes, fleas can and do jump on cats. Just like dogs, cats can come into contact with fleas through infested environments, objects, or other animals. Fleas will jump onto the cat when given the opportunity and begin feeding and reproducing.
Can Fleas Get On Clothes And Hair?

It is possible for fleas to get onto clothing and human hair. Although fleas prefer to infest animals, they can occasionally land on people and bite them in search of a blood meal. Regularly washing your clothes and maintaining good personal hygiene can help reduce the risk of fleas taking up residence on your clothing or hair.
Can Fleas Get Through Screens Or Come In Through A Window?
While it is possible for a flea to get through screens or come in through an open window, the chances are relatively low. Given their small size, fleas have difficulty climbing smooth surfaces such as window screens. However, it is still essential to maintain good home cleanliness and pet hygiene to prevent fleas from entering your home through other avenues.
Comparisons Between Fleas and Other Parasites
How Fast Do Ticks Reproduce?

Ticks reproduce at a slower rate than fleas, and their lifecycle can span multiple years. Adult female ticks can lay thousands of eggs once they have engorged on a blood meal. However, ticks move through their egg, larva, nymph, and adult stages at a much slower pace compared to fleas, usually taking months to years to complete their lifecycle.
Do Ticks Multiply Like Fleas?
While ticks have a similar reproductive method to fleas, they do not multiply as quickly. Ticks have a slower rate of reproduction and growth compared to fleas, making tick infestations less explosive in comparison. However, their potential to transmit diseases makes them a dangerous parasite.
How Fast Can Cats Reproduce Compared To Fleas?
Cats reproduce at a much slower pace than fleas. The gestation period for cats is around 60 to 67 days, and they can produce several litters in a year, with each litter containing an average of three to five kittens. Compared to fleas’ rapid reproduction rate, cats take a significantly longer time to reproduce and grow their populations.
How To Deal With Flea Infestations
How Long Does It Take To Stop The Flea Cycle?
Stopping the flea cycle depends on the effectiveness of the treatments used and the severity of the infestation. In some cases, it may take several weeks to months to break the flea cycle entirely and eliminate the infestation. This involves using flea treatments on your pets, regularly cleaning your home, and treating your outdoor environment if necessary.
How To Get Fleas Out Of Your Hair?

Discovering fleas in your hair can be a distressing experience, requiring immediate and effective action to remove these unwanted guests. Follow these steps to efficiently rid your hair of fleas and prevent their return:
- Use a Flea Comb: Carefully comb through your hair with a flea comb to remove adult fleas and their eggs.
- Wash with Anti-Flea Shampoo: Use warm water and anti-flea shampoo designed for human use, adhering strictly to the product’s instructions for safety and effectiveness.
- Treat the Source: To ensure fleas do not return, it’s crucial to address and treat the root cause of the infestation, including pets and the home environment.
What Are Some Flea Facts That Can Help In Handling Infestations?
- Fleas prefer dark, humid, and warm environments, so pay special attention to those areas when cleaning your home.
- Vacuuming your home regularly can help remove adult fleas, eggs, larvae, and pupae.
- Flea treatments formulated for pets, such as spot-on medications or oral medications, can help control and prevent infestations.
- Fleas can be carriers of various diseases, which highlights the importance of addressing infestations as quickly as possible.
Conclusion
Understanding how fast fleas reproduce is essential in controlling and preventing infestations. They have a rapid reproductive rate that, when coupled with their quick movements and jumping abilities, allows them to quickly overrun homes or pets. Effective flea management involves using pet treatments, maintaining a clean home environment, and seeking professional assistance if necessary. By being diligent and proactive, you can successfully address flea infestations and protect your pets and family.



