Fleas are notorious for their ability to torment both humans and pets alike, causing discomfort, irritation, and even triggering allergies. Understanding how long these pesky parasites can live without a host is essential for successful prevention and control efforts.
In this article, we explore the lifespan of fleas, their survival tactics, the factors that influence their longevity, and their resilience when no host is available. By gaining a deeper understanding of flea behavior and lifecycles, you can develop more effective strategies to identify, control, and prevent these relentless pests from causing havoc in your surroundings.
POINTS
- Adult fleas can survive without a host for a few days to a week, while earlier life stages (eggs, larvae, and pupae) can persist for weeks or even months in certain environmental conditions.
- Fleas cannot reproduce without a host; thus, the absence of a host will prevent the growth of the flea population, though dormant stages can quickly recover when a new host is available.
- Temperature, humidity, and the presence of organic debris in the environment significantly impact the lifespan and survival of fleas, with warm and humid conditions being the most favorable.
- The resilience and adaptability of fleas make proper pest control measures essential, targeting all life stages to effectively eradicate infestations and prevent future problems.
- Understanding the flea lifecycle and their survival tactics is key for developing comprehensive pest control approaches that ensure a flea-free home and minimize discomfort for both humans and pets.
What Is the Lifespan of a Flea?
How long do fleas generally live?

Fleas are pesky parasites that can cause discomfort and irritation to both humans and animals alike. These tiny insects typically live for about 2 to 3 months, although their lifespan can vary depending on several factors. A flea’s life begins as an egg and goes through larval and pupal stages before it becomes an adult.
What factors influence the lifespan of fleas?
Understanding the factors that influence the lifespan of fleas is crucial for effective flea control and prevention. Here, we present a concise overview of the primary factors affecting how long fleas can survive, highlighting their impact on flea lifespan.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Type of flea | Different species of fleas have varying lifespans. | The cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis, typically lives for 2 to 3 months, while other species may vary. |
| Temperature and humidity | Fleas thrive in warm, humid environments. | High temperatures and low humidity levels can significantly reduce flea lifespan. |
| Availability of food (host) | Adult fleas need to feed on blood to survive and reproduce. | Access to a host positively impacts a flea’s lifespan, allowing for continued feeding and egg production. |
| Pesticide exposure | Exposure to pesticides can affect fleas. | Pesticides may drastically shorten a flea’s lifespan through direct mortality or by affecting their reproductive capabilities. |
What is the typical life cycle of a flea?
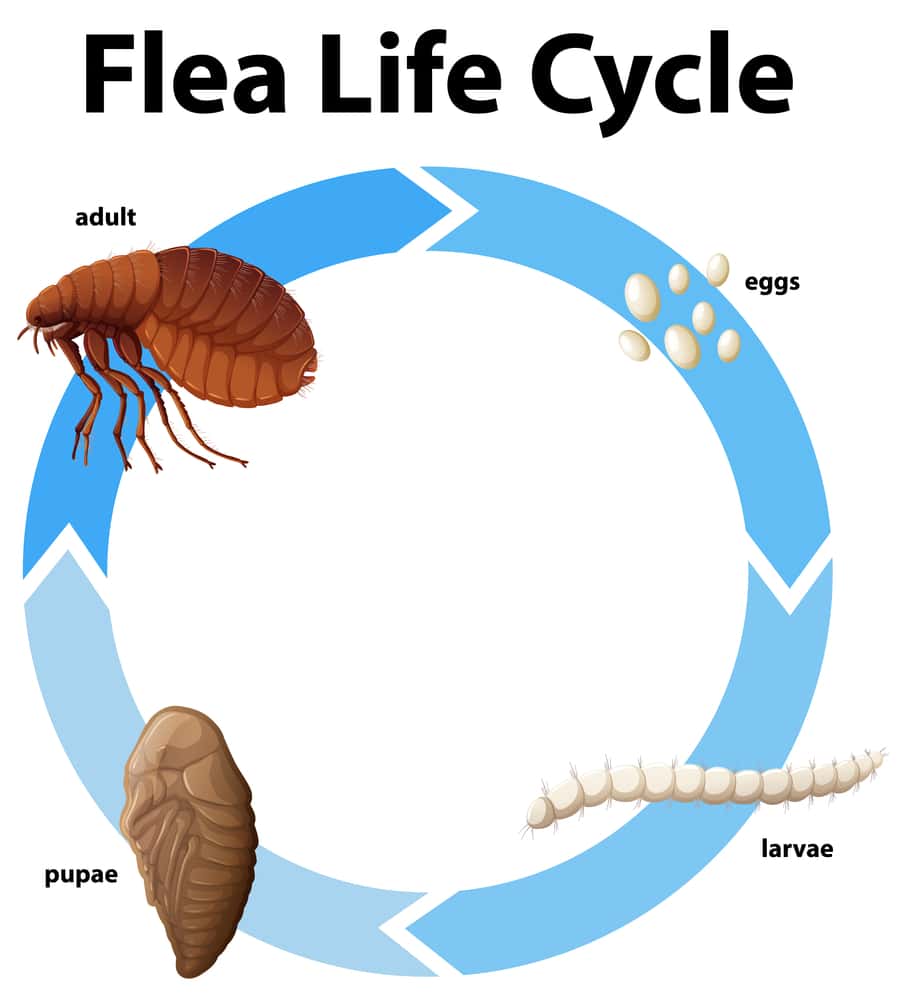
The life cycle of a flea includes four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This cycle can last anywhere from 2 weeks to several months, depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and the availability of a host.
- Egg stage: A female flea will lay her eggs on the host or in the host’s environment, such as bedding or carpet. These tiny, whitish eggs hatch in 2 to 12 days.
- Larval stage: The flea larvae, which are white and about 3-5 mm long, will feed on organic debris and adult flea feces (which contain dried blood). The larval stage lasts from 4 to 18 days, depending on environmental conditions.
- Pupal stage: After the larvae finish feeding, they spin cocoons and transform into pupae. The pupal stage can last from a few days to several weeks, depending on environmental factors. Pupae are resistant to many pest control treatments and can lie dormant for months before emerging as adults.
- Adult stage: Newly emerged adult fleas will immediately seek a host to feed on for their survival. Once they find a host, females will begin laying eggs within 24 to 48 hours.
How Long Can Fleas Survive Without a Host?
How long can fleas live without attaching themselves to a host?
Adult fleas usually must find a host within 1 to 2 days after emerging from their cocoons, where they can feed on their host’s blood for survival. However, without a host, adult fleas can survive for a few days to a week, depending on environmental conditions. Fleas in the earlier stages of their life cycle can endure longer periods without a host, as they do not require blood at that stage. The following table outlines how long fleas at each stage can last without a host.
| Life Stage | Survival Duration Without Host |
|---|---|
| Adult | A few days to a week |
| Egg | Can survive for weeks |
| Larva | Can last for weeks or even months |
| Pupa | Can remain dormant for several months |
This provides a clear understanding of the survival capabilities of fleas at each stage of their lifecycle, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive pest control strategies that target fleas at every stage of development.
Will fleas eventually die without a host, and if so, how long does it take?
Yes, fleas will eventually die without a host. As mentioned earlier, adult fleas can survive only a few days to a week without feeding on a host. After this period, they will die as a result of starvation. It’s important to note that the pre-adult stages (egg, larva, and pupa) can survive for extended periods without a host, awaiting the right conditions to hatch or emerge.
What happens to fleas if they can’t find a host?

If fleas can’t find a host, their chances of survival and reproduction are significantly decreased. Adult fleas may die of starvation, while the earlier life stages will remain in a dormant state until favorable conditions arise, such as the arrival of a suitable host. This ability to wait for the right conditions contributes to the persistent nature of flea infestations and underlines the importance of thorough pest control measures.
How Do Fleas Survive Without Pets or Human Hosts?
Fleas have developed various survival strategies to cope in environments without their preferred hosts, such as pets or humans. The table below details how long fleas can survive under such conditions, emphasizing their adaptability and the challenge they pose for pest control.
| Scenario | Survival Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| In House without pets | Several months | Earlier life stages (eggs, larvae, pupae) can remain dormant for extended periods. |
| On Humans | A few days at most | Fleas cannot reproduce on humans and do not prefer them as hosts. |
| In Carpet or other environments without pets | Weeks to several months depending on life stage | Adult fleas survive for a few days; eggs, larvae, and pupae can last much longer. |
How long can fleas survive in a house without pets?

Fleas can survive in a house without pets for several months, especially if the environmental conditions are favorable. While adult fleas may die within a week without a host to feed on, the earlier life stages (eggs, larvae, and pupae) can remain dormant for extended periods. They can survive for several months, hatching into adult fleas once they sense vibrations, heat, or carbon dioxide from the presence of a potential host.
Can fleas survive on humans, and if so, for how long?

Fleas can survive on humans, but usually for a short period. While humans are not the preferred host for fleas, they will feed on human blood if no other host is available. Fleas might also bite humans if the infestation is severe or the person accidentally comes into close contact with them. However, fleas cannot reproduce on humans, as they do not provide the right conditions for flea larvae to thrive. Typically, fleas will not remain on humans for an extended period, limiting their survival to a few days at most.
How long do fleas live in the carpet or other environments without pets?
In carpets and other environments without pets, fleas can survive for varying periods depending on their life stage and the surrounding conditions. Adult fleas can only survive for a few days to a week without feeding on a host. Conversely, flea eggs, larvae, and pupae can persist for weeks or even months in carpets or other environments. It’s important to treat these areas thoroughly with proper pest control methods to eradicate all stages of the flea life cycle.
What Happens to the Flea Population Without a Host?
Can fleas reproduce without a host, and if not, how does this affect their population?
Fleas cannot reproduce without a host, as adult fleas require blood meals from a host to lay eggs. Consequently, the absence of a host will prevent new eggs from being laid, halting the growth of the flea population. However, since flea eggs, larvae, and pupae can survive for extended periods in the environment, the flea population may quickly recover once a new host is available.
How rapidly can a flea population grow if one female finds a host?
A flea population can grow rapidly if one female flea finds a suitable host. A single female flea can produce up to 50 eggs per day and lay around 2,000 eggs during her lifetime. Assuming a high survival rate, this can lead to an exponential growth in the flea population. The ability to quickly expand their population highlights the importance of timely and effective pest control measures.
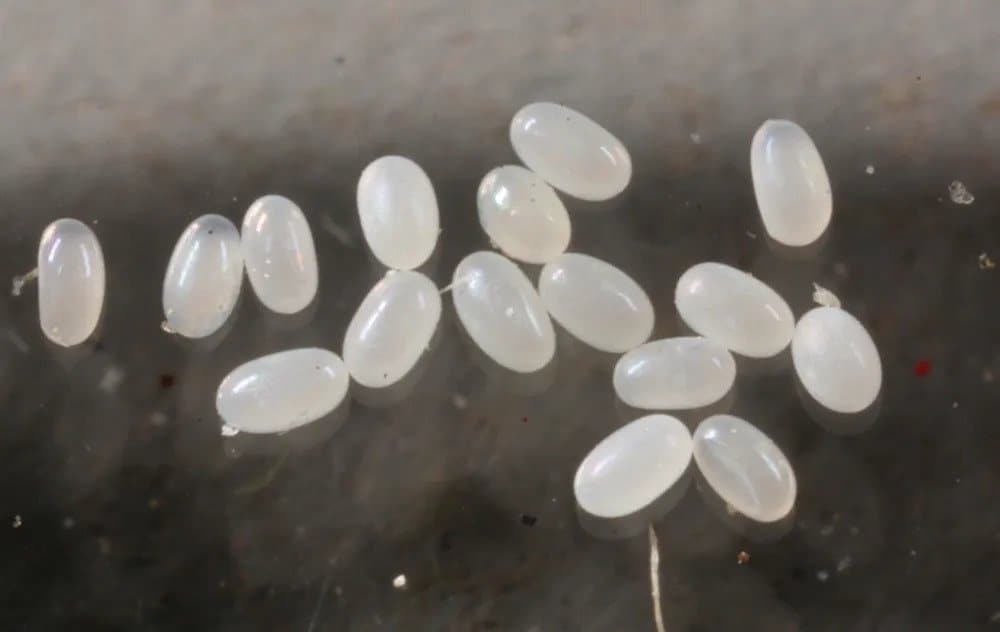

How long does it take for fleas to die out without a host, leading to the end of an infestation?
If fleas cannot find a host, they will eventually die out, leading to the end of an infestation. As previously mentioned, adult fleas without a host will die within a week, and no new eggs will be laid. However, flea eggs, larvae, and pupae can survive for weeks or months in the environment. It may take several months for all life stages of fleas to die out in the absence of a host, effectively ending the infestation.
Are There Any Differences in the Lifespan of Fleas Based on Their Environment?
Does the lifespan of a flea without a host differ from one that finds a host?
The availability of a host plays a critical role in determining the lifespan of fleas. The table below compares the lifespan of fleas when they have access to a host versus when they are deprived of one, illustrating the impact of host availability on flea survival.
| Condition | Lifespan Duration |
|---|---|
| With Host | Up to 2 to 3 months |
| Without Host | A few days to a week for adults; pre-adult stages (egg, larva, pupa) can survive significantly longer without a host |
How does a flea’s environment affect its lifespan, with or without a host?
A flea’s environment can significantly affect its lifespan, whether it has a host or not. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and the availability of food sources, like organic debris and adult flea feces for larvae to consume, play a crucial role. Fleas typically thrive in warm, humid environments. High temperatures and low humidity can shorten a flea’s lifespan.
What environmental conditions can lead to fleas surviving longer without a host?
Fleas can survive longer without a host in certain environmental conditions. Greater survival rates are associated with the following factors:
- Warm temperatures: Fleas can survive better in warm environments, with an optimal temperature range of 70°F to 85°F (21°C to 29°C).
- High humidity: A relative humidity of 70% or higher is optimal for flea survival, as lower humidity levels can cause the flea eggs and larvae to dry out.
- Availability of organic debris: The presence of organic matter for flea larvae to feed on can increase their chances of survival.
Conclusion
Recap of how long fleas can live without a host
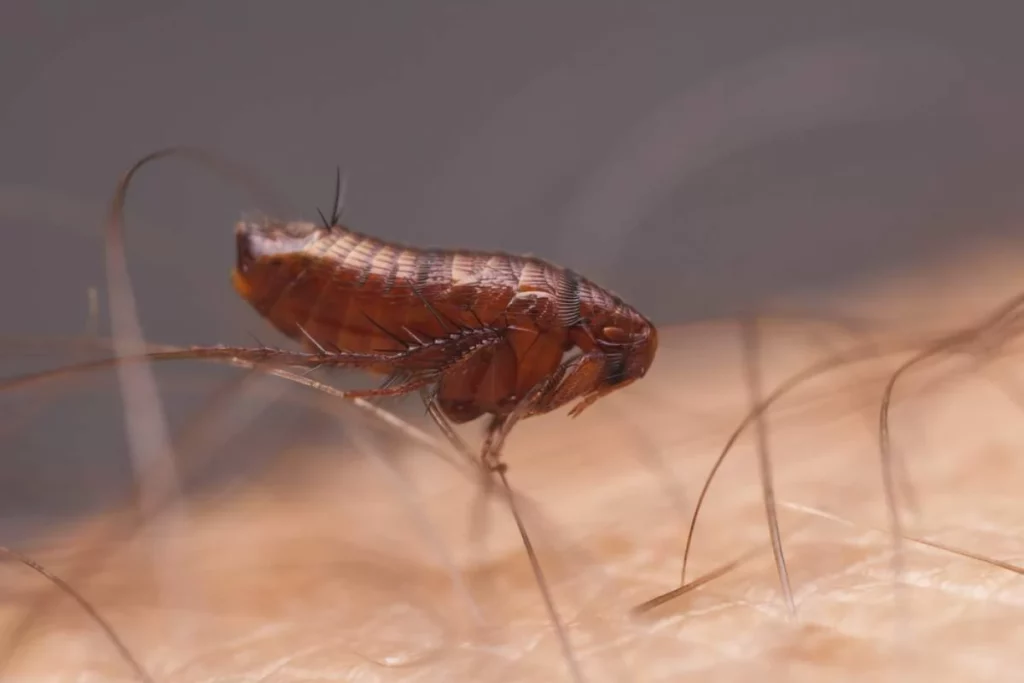

The ability of fleas to survive without a host depends on their life stage and the environmental conditions they find themselves in. Adult fleas can survive without a host for a few days to a week, whereas earlier life stages (eggs, larvae, and pupae) can linger for weeks or even months in certain conditions. A warm, humid environment with enough organic debris offers fleas a greater chance of survival without a host.
Importance of understanding flea lifecycles and survival tactics for effective flea control
Understanding the flea lifecycle and their survival tactics is critical for effective flea control. Since fleas can survive for extended periods without a host, especially in their pre-adult stages, it is essential to employ thorough, long-term treatment strategies to target all life stages. This understanding also emphasizes the importance of preventative measures, such as regular cleaning and grooming pets, to minimize the chances of a flea infestation in your home.
The resilience and adaptability of fleas
Fleas are incredibly resilient and adaptable pests that can cause discomfort and irritation to humans and animals alike. Their ability to survive without a host in various environmental conditions reflects their persistence and highlights the challenges in eradicating flea infestations. By understanding their lifecycle and survival tactics, we can develop comprehensive pest control approaches that target each stage of their development, making our homes flea-free and comfortable for ourselves and our pets.



