Fleas may be tiny parasites, but they can cause significant discomfort and carry various diseases that can affect both humans and animals.
In this article, we will explore the dangers posed by fleas, the diseases they can transmit, and their impact on the health of people and pets. Furthermore, we will discuss the importance of flea control and prevention measures to limit the spread of diseases carried by these parasites while ensuring the health and well-being of your household.
POINTS
- Fleas are dangerous parasites that can transmit various diseases to humans and animals, including bubonic plague, murine typhus, and Bartonellosis.
- Flea bites can cause itchiness, allergic reactions, and potentially skin infections due to excessive scratching.
- Pets, such as cats and dogs, can experience flea allergy dermatitis, tapeworms, anemia, or Bartonellosis when infested with fleas.
- Practicing effective flea control and prevention measures, like using vet-recommended treatments on pets and maintaining a clean home and yard, can significantly reduce the risk of flea-borne diseases.
- Seeking professional help for severe or persistent flea infestations can help protect the health of your family and animals.
Introduction to Fleas as Parasites

Are Fleas Considered Parasites?
Yes, fleas are considered parasites because they live on the bodies of their hosts, which can be both humans and animals, and feed on their blood. Fleas rely on their hosts for survival, making them a classic example of parasites.
Why are Fleas Considered Dangerous?
Fleas are considered dangerous for several reasons. Their bites can cause itching and discomfort for both humans and animals, and scratching flea bites can lead to skin infections. Additionally, fleas can transmit a variety of diseases to both people and pets, some of which can have severe health implications.
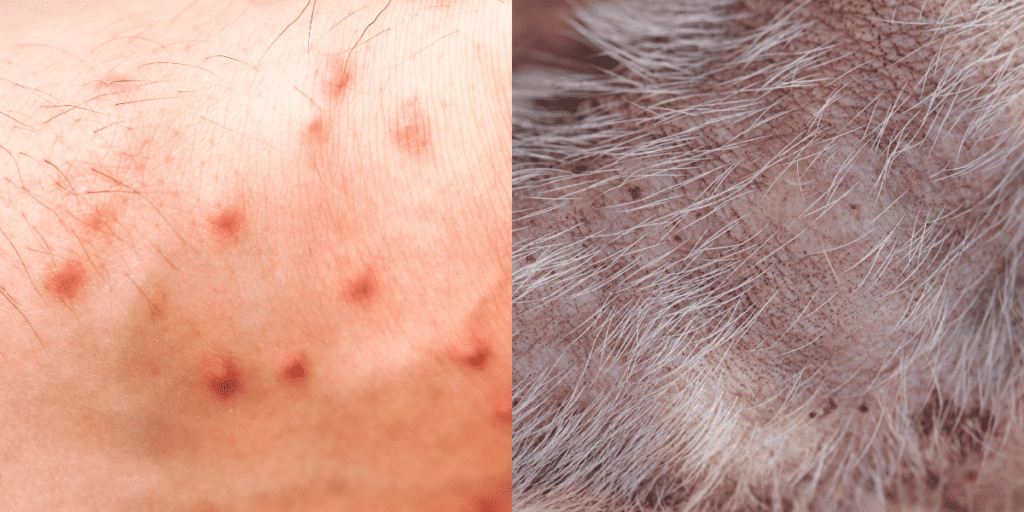
Are Fleas Dangerous to Humans and Animals?
Fleas are dangerous to both humans and animals because of their potential to transmit diseases, cause allergic reactions, and contribute to other health issues, such as anemia and skin infections.
Understanding the Potential for Fleas to Affect Humans
Can Fleas Transfer to Humans?
Yes, fleas can transfer to humans from animals or their environment. However, human-flea infestations are not as common as those involving pets like cats and dogs. Fleas may bite humans when their preferred hosts, such as pets, are unavailable.
How Do Humans Get Fleas?
Fleas can infest humans in several ways, often making their way from animals or infested environments. Understanding these common pathways is crucial for preventing and managing flea infestations effectively.
- Contact with Infested Animals: Direct interaction with pets or animals that are already carrying fleas.
- Their Living Spaces or Household Items: Being in environments where infested animals live or have access to, including homes, bedding, and furniture.
- Hitching a Ride on Clothing: Fleas can attach themselves to your clothes when you are in an infested area.
- From Infested Furniture, Carpets, or Bedding: Coming into contact with items that are harboring fleas.
- Jumping from One Host to Another: Fleas have the ability to jump significant distances, allowing them to move easily from pets or wildlife to humans.
Can Humans Catch Fleas From Pets like Cats and Dogs?
Yes, humans can catch fleas from pets like cats and dogs. If your pet is infested with fleas, the insects can jump onto you and bite in search of their next blood meal. It is crucial to treat your pet for fleas to prevent infestations and protect your family’s health.
Can Fleas be Transferred to Humans from Other Animals, like Squirrels?
Yes, fleas can be transferred to humans from other animals, including squirrels. While less common, fleas may infest wild animals, which can, in turn, pass fleas onto humans who come into contact with them or their living spaces. To avoid this, it is essential to keep a safe distance from wild animals and maintain a clean outdoor living space.
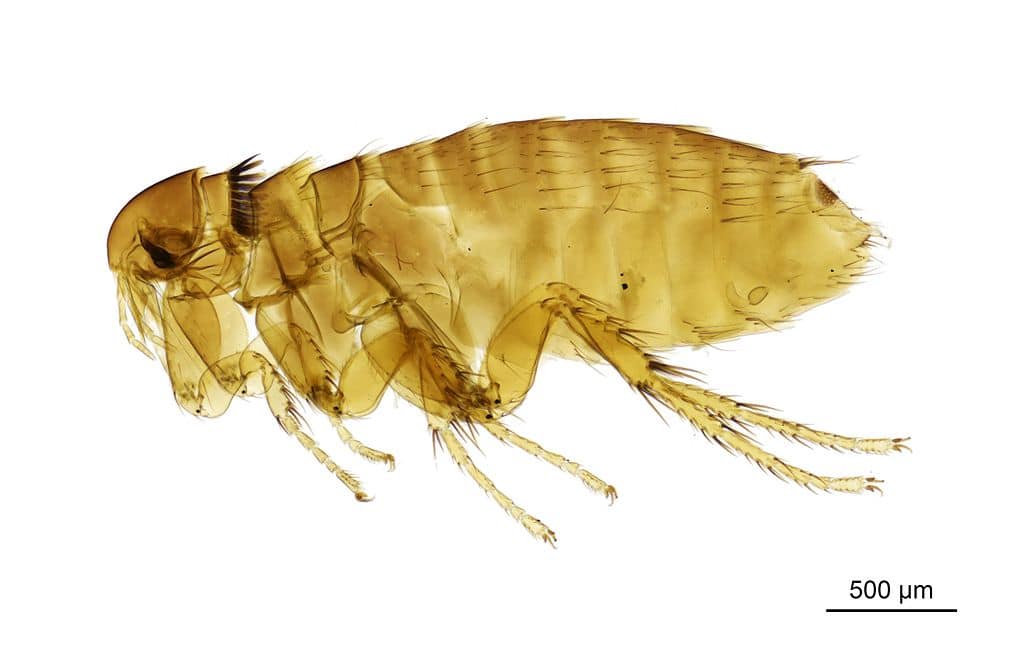

Can Fleas Make Humans Sick?
What Happens to a Human Infected by Fleas?

When a human is infected by fleas, they may experience flea bites that cause itchiness, redness, and irritation. While these symptoms are typically mild, excessive scratching can potentially lead to skin infections. Moreover, fleas can transmit various diseases, some of which can have serious health implications, as will be discussed in the following sections.
Can Humans Get Sick from Flea Bites?
Humans can get sick from flea bites due to allergic reactions, skin infections, or the transmission of diseases carried by the fleas. Some individuals may be more sensitive to flea bites and experience more severe allergic reactions, while others may only experience mild itching and discomfort.
Can Flea Bites Spread Disease in Humans?
Yes, flea bites can spread diseases in humans. When a flea bites a host, it can potentially inject pathogens into the host’s bloodstream, leading to infection.
Understanding the Diseases Fleas Can Carry and Their Implications
What Diseases Do Fleas Carry to Humans?
Fleas are tiny parasites that can transmit a range of diseases to humans, leading to various health issues. Below is a table summarizing key diseases carried by fleas, highlighting their symptoms and the primary method by which they are transmitted to humans.
| Disease Name | Symptoms | Transmission Method |
|---|---|---|
| Bubonic Plague | Fever, chills, weakness, swollen lymph nodes | Bites from infected Oriental rat fleas |
| Murine Typhus | Fever, headache, rash | Flea feces on scratched skin |
| Tungiasis | Painful sores, itching, inflammation | Burrowing of sand fleas into skin |
| Bartonellosis (Cat-scratch disease) | Fever, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue | Flea feces on scratches or bites |
| Dipylidium Caninum (tapeworm) | Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, weight loss | Ingesting infected fleas |
Do Fleas Carry Lyme Disease?
Fleas do not typically transmit Lyme disease. Lyme disease is most commonly transmitted through the bites of infected ticks, particularly deer ticks and black-legged ticks.
Can Fleas Give Humans Worms?
Fleas can transmit a specific type of tapeworm called Dipylidium caninum. This tapeworm typically affects dogs and cats but can also infect humans, especially children, who accidentally ingest an infected flea.
List of Flea-Borne Diseases
The following is a list of some common flea-borne diseases:
- Bubonic plague
- Murine typhus
- Tungiasis
- Bartonellosis (Cat-scratch disease)
- Flea-borne spotted fever (Rickettsia felis infection)
- Dipylidium caninum (tapeworm)
Are There Any Deadly Diseases Transmitted by Fleas?

Yes, fleas can transmit deadly diseases such as the bubonic plague. While rare in modern times, the bubonic plague has historically caused widespread pandemics with high mortality rates. Proper pest control measures, hygiene practices, and antibiotic treatments have significantly reduced the prevalence and lethality of such diseases today.
Fleas’ Effects on Animals
What Diseases Do Fleas Carry to Dogs and Cats?
Fleas are not just a nuisance for pets; they can transmit several serious diseases to dogs and cats, affecting their health and quality of life. The table below outlines the key diseases fleas carry to our furry friends, highlighting the health implications for each species.
| Disease Name | Affects | Symptoms in Dogs | Symptoms in Cats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flea Allergy Dermatitis | Dogs, Cats | Itching, redness, hair loss, skin lesions | Itching, redness, hair loss, skin lesions |
| Tapeworm (Dipylidium caninum) | Dogs, Cats | Weight loss, visible tapeworm segments in feces | Weight loss, visible tapeworm segments in feces |
| Anemia | Dogs, Cats | Lethargy, pale gums, weakness | Lethargy, pale gums, weakness |
| Bartonellosis (Cat-scratch disease) | Dogs, Cats | Rarely symptomatic in dogs | Fever, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue |
Can Fleas Make a Cat Sick?

Yes, fleas can make a cat sick. Flea-infested cats can experience flea allergy dermatitis, tapeworms, anemia, or Bartonellosis. It is crucial to protect your cat against fleas to maintain their well-being.
Can Cats Get Sick from Fleas?
Yes, cats can get sick from fleas not only because of the flea bites themselves but also due to the various health complications discussed above, such as an allergic reaction, tapeworm infection, or Bartonellosis.
How to Protect Against Flea-Borne Diseases
What are the Dangers of Flea Infestations?
Flea infestations pose various dangers to both humans and animals, including:
- Discomfort and itchiness caused by flea bites
- Allergic reactions and potential skin infections
- Transmission of various diseases
- Anemia in animals, especially when dealing with heavy infestations
How to Control Flea Infestations?
Controlling flea infestations involves a combination of preventive measures and targeted treatments. Some effective strategies include:
- Regularly treating your pets with vet-recommended flea control products, such as topical treatments, oral medications, or flea collars
- Vacuuming your home frequently to eliminate flea eggs, larvae, and adults
- Washing your pet’s bedding, toys, and personal items regularly in hot water
- Keeping your outdoor living spaces clean and maintaining a tidy yard to avoid providing breeding grounds for fleas
- Consulting with a pest control professional if your infestation is severe or persistent
Can Flea Extermination Prevent Diseases?
Flea extermination can significantly reduce the likelihood of flea-borne diseases affecting you or your pets. By effectively controlling flea populations and preventing infestations, you minimize the chances of disease transmission and protect the health of your family and animals.
What are the Best Practices for Flea Pest Control?
The best practices for flea pest control include:
- Consistently using vet-recommended flea prevention and treatment products on your pets
- Keeping your home clean, including regular vacuuming and washing pet items, to eliminate fleas and their eggs
- Maintaining a clutter-free and clean yard that discourages fleas from breeding
- Seeking professional help for serious or persistent infestations
FAQ
How common is it to get sick from fleas?
While not extremely common, getting sick from fleas can happen, especially if you have an infested pet or live in an area with a high flea population. Practicing proper flea control measures can significantly reduce the risk of contracting a flea-borne disease.
What parasites do fleas carry?
Fleas can carry several parasites such as the tapeworm Dipylidium caninum, which can infect both pets and humans. Protecting your pets from fleas can help reduce the chances of parasite transmission.
Are flea bites poisonous?
Flea bites are not poisonous, but they can cause irritation, itching, and potential allergic reactions. In some cases, excessive scratching can lead to skin infections. Moreover, flea bites can transmit diseases carried by fleas.
Conclusion
Recap of the Diseases Fleas Carry and Their Impact on Humans and Animals
Fleas are not only a nuisance but also carriers of several diseases that can affect humans and animals. These diseases range from bacterial infections like bubonic plague and Bartonellosis to parasitic infestations like tapeworm. Fleas can also cause allergic reactions, skin infections, and anemia in both pets and humans.
The Importance of Flea Control and Prevention Measures to Limit the Spread of Diseases
To protect your family and pets from flea-borne diseases, it is essential to practice effective flea control and prevention measures. Regularly treating your pets with vet-recommended products, maintaining a clean home and yard, and seeking professional help for severe infestations can go a long way in limiting the impact of fleas on your household’s health and well-being.



