When it comes to household pests, fleas are a common concern for pet owners and non-pet owners alike. These notorious parasites can cause itchiness, discomfort, and even illness in both animals and humans. Gaining insight into the feeding habits of fleas is essential in understanding how to identify, control, and prevent them effectively.
In this article, we will explore the diet of fleas, how they consume their food, and how their feeding habits impact their hosts. Additionally, we will discuss various animals and organisms that interact with fleas, unique characteristics and behaviors related to their feeding, and ways to prevent them from feasting on you and your pets. Let’s dive into the world of fleas to better protect ourselves and our furry companions.
POINTS
- Fleas primarily feed on the blood of warm-blooded animals, such as cats, dogs, rodents, and birds, but can also survive on humans when necessary. However, they cannot reproduce solely on human blood.
- Flea larvae have a different diet, feeding on organic debris and feces, which contain undigested blood, instead of directly consuming blood like adult fleas.
- Flea infestations can cause a range of issues in pets, such as itchiness, skin inflammation, fur loss, and even anemia. In humans, flea bites can lead to itching, redness, and even serious allergic reactions to their saliva.
- Fleas have natural predators, including ants, spiders, and certain bird species, which prey on both adult fleas and their eggs.
- Preventing flea infestations involves regular flea treatments for pets, grooming, maintaining a clean home environment, and eliminating potential flea breeding grounds.
What is the Basic Diet of Fleas?
Understanding the dietary habits of fleas is crucial for controlling and preventing infestations in your home and on your pets. Below is a table that breaks down the basic diet of fleas, distinguishing between adult fleas and their larvae to offer clear insights.
| Life Stage | Diet | Diet Source |
|---|---|---|
| Adult Fleas | Blood | Warm-blooded animals (cats, dogs, rodents, birds, and humans) |
| Flea Larvae | Organic debris and feces | Undigested blood from adult flea feces, dead skin, hair, and other organic particles |
What do fleas generally eat?

Fleas are parasites that generally feed on the blood of their mammalian hosts. The most common hosts for fleas are warm-blooded animals such as cats, dogs, rodents, and birds. However, they are not picky and may also feed on the blood of humans if their preferred hosts are not available.
What do fleas feed on besides blood?
The primary diet of adult fleas consists of blood from their hosts. However, flea larvae, which are a different life stage of the flea, feed on organic debris, including flea feces that are rich in undigested blood.
Can fleas survive on human blood?
Yes, fleas can survive on human blood if their preferred hosts are not available. Although they prefer to feed on the blood of pets such as cats and dogs, they will feed on humans when necessary. However, fleas cannot reproduce solely on human blood.
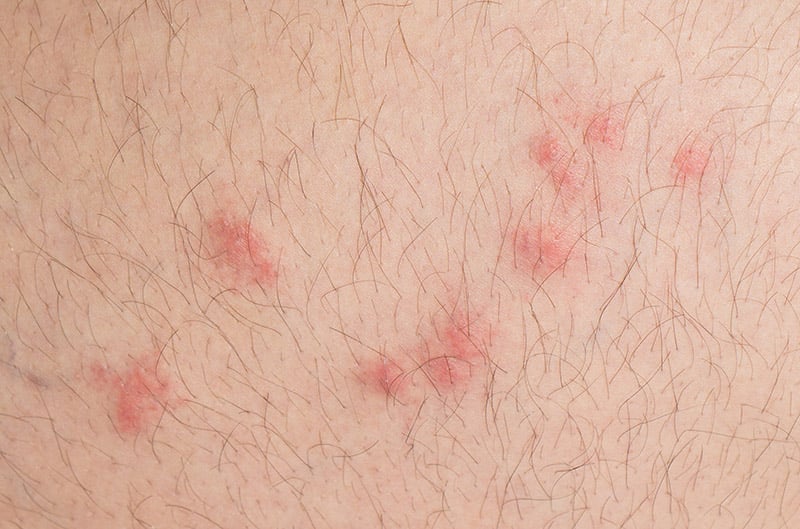
What type of blood do fleas prefer?
Fleas are adaptable parasites and can feed on a variety of blood sources. However, they have preferences based on the type of species they infest. For example, cat fleas prefer feeding on cats and dog fleas prefer dogs. That said, they will feed on any readily available host if their preferred blood source is not accessible.
How often do fleas need to eat?
Adult fleas need to feed regularly to survive and reproduce. Female fleas consume more blood than males as they require extra nourishment to produce eggs. A female flea can consume up to 15 times her body weight in blood daily, while a male flea feeds less often. In general, adult fleas feed every few hours.
How Does the Flea Diet Vary Across Different Life Stages?
What do flea larvae eat?
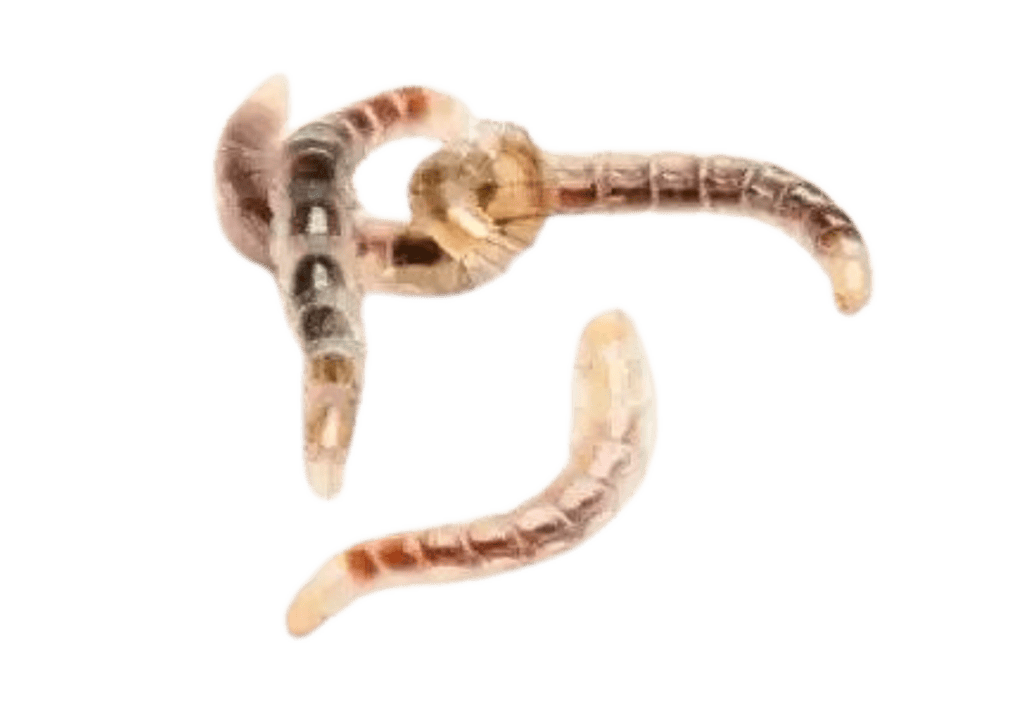
Flea larvae have a unique diet compared to their adult counterparts, focusing on the consumption of various organic materials available in their environment. Here are the specifics of what they feed on:
- Organic debris found in their environment.
- Flea feces, rich in undigested blood.
- Dead skin, hair, and other organic particles.
- Occasionally, the eggs of other fleas, depending on the availability of other food resources.
Do baby fleas bite, and what do they feed on?
Baby fleas, also known as larvae, do not bite or consume blood directly. Instead, they rely on the organic debris and feces of adult fleas, which contain undigested blood, for their sustenance and growth.
How does the diet of mature fleas differ from that of larvae and baby fleas?
Mature fleas, both male and female, feed directly on the blood of their hosts. This differs from the diet of larvae, as they consume organic debris and fecal matter. Blood is essential for adult fleas to survive, while larvae depend on organic material for growth and development.
How do Fleas Consume Their Food?
How do fleas eat and drink?
Fleas have a specialized method of consuming food that allows them to efficiently feed on their hosts. The table below outlines the process by which fleas eat and drink, highlighting their adapted mouthparts and feeding behavior.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Mouthparts | Sharp, needle-like structures called stylets for piercing skin; saliva contains anticoagulants. |
| Feeding Process | Fleas pierce the skin to access blood, using their tube-like food canal to suck blood directly from capillaries. |
| Selection of Feeding Spot | Prefer areas with thin skin and good blood flow; detected through host’s heat and carbon dioxide emissions. |
| Duration of Feeding | Can spend several minutes to hours feeding, depending on hunger level and availability of blood. |
How do fleas feed?
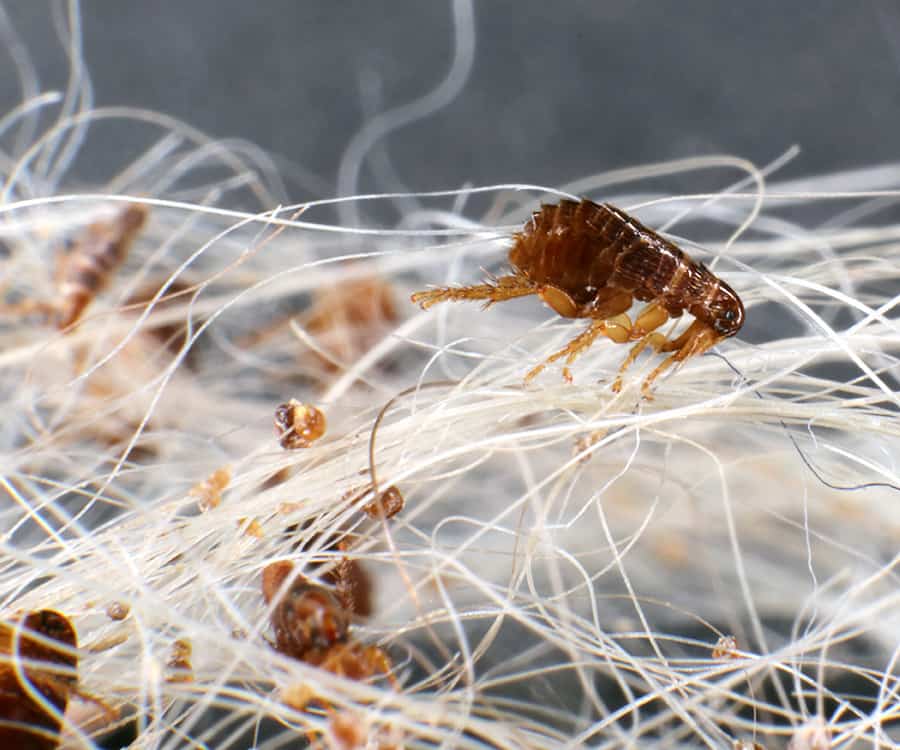

When fleas feed, they first locate a suitable host through heat and carbon dioxide detection. Once they are on a host, fleas move around in search of an ideal feeding spot, generally choosing an area with thin skin and good blood flow. After biting their host, they spend several minutes to hours feeding, depending on factors like the availability of blood and how hungry they are.
Do fleas suck blood or eat it?
Fleas suck blood directly from their host’s capillaries with their tube-like food canal. Once the stylets pierce the skin and tap into a capillary, they use their specialized mouthparts to consume the blood.
How Does the Flea Diet Affect their Hosts?
Can fleas feed off humans?

Although fleas prefer to feed on pets like cats and dogs, they are opportunistic parasites and can also feed on humans when their preferred hosts are not available. Human blood can support a flea’s survival, but it is not the ideal food source for their reproduction.
Do dog fleas go on humans, and what impact does their feeding have on human hosts?
Dog fleas, like other species of fleas, can bite humans if their preferred host is not available. Flea bites on humans can cause itchiness, redness, and inflammation. In some cases, people may also experience allergic reactions to flea saliva, leading to more severe symptoms like swelling, hives, and breathing difficulties.
Do fleas prefer certain blood types in humans?
There is currently no scientific evidence to suggest that fleas have a preference for specific human blood types. They are more likely to feed on a human host based on factors like body temperature, carbon dioxide emissions, and the accessibility of blood vessels near the skin’s surface.
How does a flea feeding affect pets like dogs and cats?
Fleas can cause a variety of issues in pets, such as itchiness, redness, and skin inflammation. Pets who are infested with fleas may scratch and bite themselves excessively, which can lead to fur loss and skin infections. Flea infestations can also cause anemia in pets, especially in young or weakened animals, due to the loss of blood.

Can fleas make a dog not eat or display other behavioral changes?
Fleas can cause a great deal of discomfort to a dog, which may result in changes to their behavior, such as excessive scratching, biting, or licking. In some cases, the distress caused by fleas may lead to a lack of appetite or overall decreased energy levels. It is essential to address a flea infestation promptly to prevent further complications in your pet’s health and well-being.
What Other Animals or Organisms do Fleas Interact With, and How Does Their Diet Play a Role?
What animals eat fleas?
Fleas, despite being pests to humans and their pets, are a food source for various animals and insects in the ecosystem. Here’s a look at the natural predators that include fleas in their diet:
- Insects and Arachnids:
- Ants (specific species)
- Beetles
- Lacewings
- Centipedes
- Spiders
- Mites
- Birds:
- House sparrows
- Chickens (they feed on fleas by pecking or scratching at the ground to dislodge the insects)
Do cats or dogs ever eat fleas?
Cats and dogs may inadvertently consume fleas while grooming themselves. This is not a common or effective way to control fleas, as the primary issue is the flea’s bite and their presence on the host, rather than the consumption of the pests.
Do ants and spiders eat fleas?
Ants, particularly fire ants, can prey on fleas by attacking and consuming both the eggs and the adult fleas. Spiders may also eat fleas, particularly when they are trapped in their webs.
Can fleas live and feed on other animals besides cats and dogs?
Fleas are not just a problem for cats and dogs; they can live and feed on a variety of other animals as well. Here’s an overview of their flexibility in hosts:
- Rodents.
- Birds
- Livestock, including sheep, goats, and cattle.
Fleas generally prefer furry animals, which provide a conducive environment for their reproduction and survival.
What Unique Characteristics or Behaviors Do Fleas Have Related to Their Feeding Habits?
Can fleas reproduce with human blood?
Fleas can survive on human blood, but it is not the ideal food source for their reproduction. Female fleas need the blood of their preferred host species, such as cats or dogs, to reproduce successfully. If they feed exclusively on human blood, they may not lay eggs or produce fewer offspring.
Do fleas only live on animals they can feed on?

Fleas prefer to live on animals that provide a suitable habitat and constant food source, such as cats and dogs. However, they can temporarily feed on other hosts like humans and different types of animals when their preferred blood source is not available.
How long can a flea live without eating?
Adult fleas can survive without feeding for several days to two weeks, depending on factors such as temperature and humidity. However, their ability to reproduce decreases significantly without a steady source of blood.
Do fleas leave behind any trace of their feeding, such as feces?
Fleas do leave fecal matter behind after feeding, which is often referred to as “flea dirt.” Flea dirt consists of tiny, dark specks of digested blood and can be found on a host’s skin or bedding. It serves as a primary food source for flea larvae.
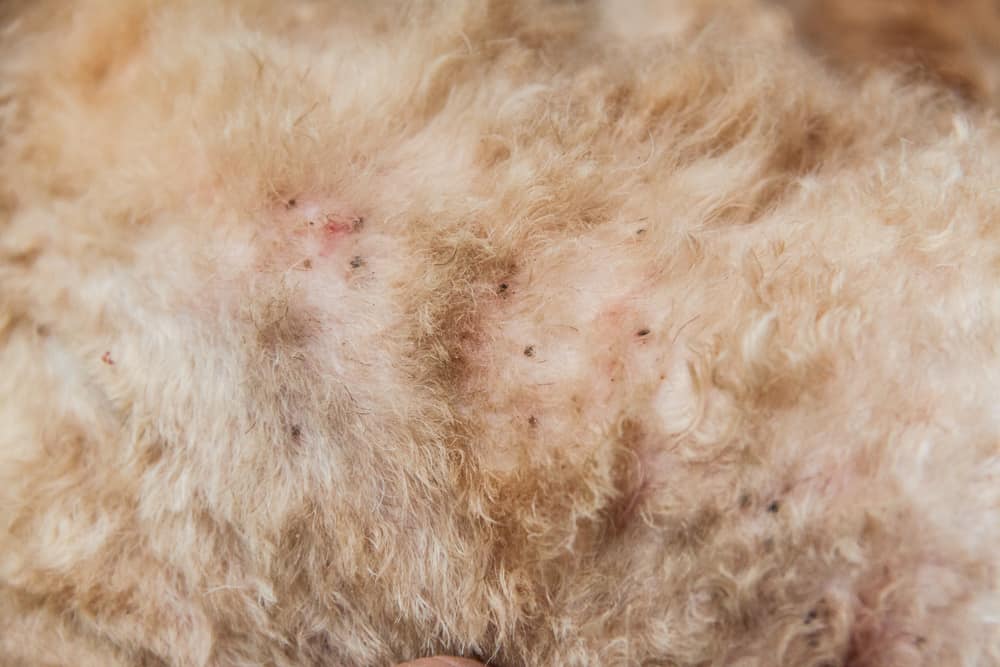
Why do fleas bite humans and what determines who they bite?
Fleas bite humans when their preferred host is not available, or there is a high population of fleas competing for food. Factors like body temperature, carbon dioxide emissions, and the proximity of blood vessels to the skin’s surface can influence who a flea might bite.
How Can Humans and Pets Prevent Fleas from Feeding on Them?
What can I eat or drink to keep fleas from biting me?
There is no foolproof dietary trick to prevent fleas from biting you. The best approach to keeping fleas at bay is through regular preventative measures, such as:
| Preventive Measure | Description | Applicable To |
|---|---|---|
| Flea Control Products | Use of spot-on treatments, oral medications, or flea collars to prevent flea infestations. | Pets |
| Regular Grooming | Routine grooming helps to detect and remove fleas from pets before they can spread. | Pets |
| Clean Bedding and Living Spaces | Regularly wash pet bedding and vacuum living areas to remove flea eggs, larvae, and adults. | Pets and Human Areas |
| Environmental Maintenance | Eliminate potential flea breeding grounds by keeping your yard clean and free of debris. | Outdoor Areas |
| Flea Prevention for Humans | While direct treatments are rare, maintaining a clean environment and treating pets can reduce human risk. | Humans (indirectly) |
Can fleas live off humans and how can humans protect themselves?
While fleas can feed on humans, they cannot reproduce and thrive solely on human blood. To protect yourself from fleas, focus on flea prevention for your pets and home. Using flea control products on your pets and maintaining a clean living environment can significantly reduce the risk of flea infestations.
Do fleas go on people and how can this be prevented?
Fleas can bite people, particularly when their preferred host is not available. Preventing fleas from getting on people involves regular flea treatments for your pets and maintaining a clean home environment by vacuuming, washing pet bedding, and eliminating potential flea breeding grounds.

How to handle fleas on pets and can fleas jump from pets to humans?
Managing fleas on pets is crucial not only for their health but also to prevent these pests from jumping or transferring to humans. Here are effective strategies for flea control and prevention:
- Flea Control Products:
- Use spot-on treatments.
- Administer oral medications.
- Employ flea collars.
- Regular Grooming and Cleaning:
- Groom your pets regularly.
- Clean their bedding and living spaces thoroughly.
Conclusion
Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the feeding habits and preferences of fleas is crucial in mitigating the risk of infestations and alleviating the discomfort they cause to both humans and pets. By employing a combination of effective flea control products, regular grooming of pets, and maintaining a clean living environment, you can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing flea-related issues. It’s essential to remain vigilant, proactive, and consistent in your strategies to keep your family, including your pets, happy, healthy, and flea-free.



