Cockroaches and beetles differ significantly in behavior, habitat, and physical characteristics. This article delves into these differences, helping you identify which pest you might be dealing with and why accurate identification is crucial for effective control.
POINTS
- Cockroaches and beetles can be differentiated by physical characteristics such as body shape, size, color, and antennae, with cockroaches typically having a flatter body and longer antennae, while beetles have more varied shapes and often harder exoskeletons.
- Common beetles mistaken for cockroaches include ground beetles, June beetles, and furniture beetles, which share similar sizes and coloring, leading to misidentification.
- Cockroaches prefer warm, humid environments and are nocturnal, posing health risks due to their potential to carry bacteria and trigger allergies, whereas beetles have diverse habitats and are less likely to cause health issues but can damage household items.
- Scientific classification places cockroaches in the order Blattodea and beetles in Coleoptera, with cockroaches being ancient insects closely related to termites, and beetles being the largest order of animals with a wide range of adaptations.
- Both cockroaches and beetles play important ecological roles, with cockroaches involved in decomposition and beetles serving as pollinators, predators, and decomposers, but their interaction with humans varies from beneficial to pestiferous.
Cockroach vs. Beetle: Identifying Key Differences and Common Confusions
When you spot a scuttling insect in your home, it’s natural to wonder if you’re dealing with a cockroach or a beetle. Both pests can be unwelcome guests, but there are key differences that can help you determine which has made its way into your space. Let’s delve into the characteristics that set these insects apart.
Physical Characteristics: Body Shape, Size, and Color
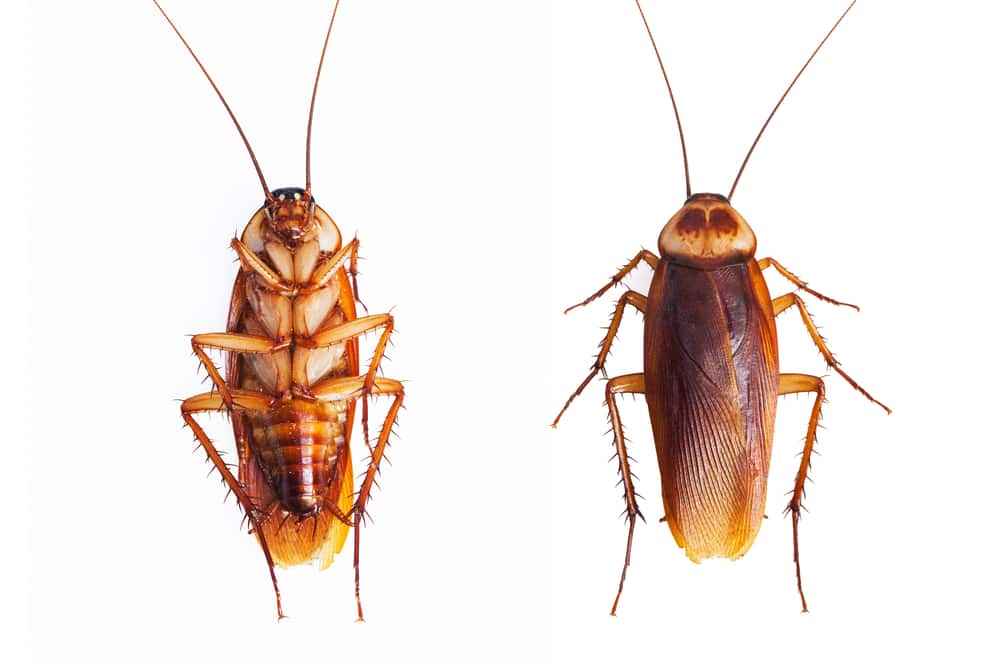
The first step in distinguishing a cockroach from a beetle is to examine their physical features. Cockroaches typically have a flat, oval-shaped body with long antennae and six legs. They are usually brown or black and have a somewhat greasy appearance.

In contrast, beetles have more varied body shapes but are generally more rounded or dome-shaped. They often have hard exoskeletons with distinct coloring that can include bright patterns or metallic hues.
Size is another factor. While both insects come in various sizes, cockroaches tend to be larger on average. For instance, the common American cockroach can grow up to 1.6 inches in length, whereas many beetles are smaller.
Color can also be a clue, but it’s not always reliable since both cockroaches and beetles come in a range of colors. However, if you see an insect with bright colors or intricate patterns on its back, it’s more likely a beetle.
Beetles Often Mistaken for Cockroaches
Several beetle species are frequently mistaken for cockroaches due to their similar size and coloring. The most common culprits include:

Ground Beetles: These beetles are dark, sometimes black, which can cause them to be mistaken for cockroaches. However, ground beetles have hard wing covers and a more rounded shape.

June Beetles: Also known as June bugs, these beetles are typically brown and can appear similar to cockroaches at a glance. They are distinguished by their thick, hard bodies and slow movement.

Furniture Beetles: These small, brown beetles might be confused with baby cockroaches, but furniture beetles have a cylindrical body shape and are wood-boring insects.
The confusion often stems from a lack of familiarity with the insects’ appearances and behaviors. By learning the specific traits of each, you can more easily identify whether you’re dealing with a beetle or a cockroach.
Habitat, Behavior, and Infestation: Roaches vs Beetles in Homes
Understanding the preferred habitats and behaviors of these pests can also aid in identification and control.
Typical Habitats and Behaviors
Cockroaches are often found in warm, humid environments and are notorious for their nocturnal activities. They tend to hide in dark, secluded areas during the day and are attracted to food remnants and water sources.
Beetles, on the other hand, have a wider range of habitats. While some may enter homes, they are just as likely to be found outdoors. Beetles are not typically drawn to the same living conditions as cockroaches and are more diverse in their dietary needs, depending on the species.
Health Implications and Challenges of Infestations
Cockroaches are known carriers of bacteria and can trigger allergies and asthma, making their control a significant concern for homeowners. Their ability to breed rapidly and remain hidden can make infestations particularly challenging to eradicate.
Beetle infestations are generally less hazardous to human health, but certain species can cause damage to furniture, clothing, or stored food products. While beetles do not multiply as quickly as cockroaches, they can still be a nuisance and require different control strategies.
By recognizing the different habitats and behaviors of cockroaches and beetles, you can take the first steps in addressing any pest issues in your home.
Taxonomy and Species Specifics: Understanding the Scientific Distinctions
To fully grasp the differences between cockroaches and beetles, it’s helpful to look at their scientific classifications. This information can shed light on why these insects are distinct from one another and help you identify them more accurately.
Scientific Classification of Cockroaches and Beetles
Cockroaches belong to the order Blattodea, which includes termites as their close relatives. They are part of the insect class Insecta and have been on Earth for millions of years, with fossil evidence dating back to the Carboniferous period.
Beetles, meanwhile, are classified under the order Coleoptera, which is the largest order in the animal kingdom. They are also part of the class Insecta and are known for their hardened forewings, which protect their flying wings underneath.
Specific Species and Their Unique Characteristics
Within these orders, there are several species of note:
- American Cockroach (Periplaneta americana): One of the largest species of cockroaches, the American cockroach is reddish-brown and can fly short distances.
- German Cockroach (Blattella germanica): A smaller species, the German cockroach is light brown and has two dark stripes on its back. It’s one of the most common roaches found in homes.
In the world of beetles:
- Ground Beetle (Carabidae): These beetles are often black or metallic and have ridged wing covers. They are beneficial insects, preying on garden pests.
- Black Carpet Beetle (Attagenus unicolor): This beetle is a common household pest, feeding on natural fibers and can be identified by its shiny black body and brown legs.
By familiarizing yourself with these species and their characteristics, you can better identify what’s in your home and take appropriate action.
Visual Identification and Misidentification Issues in Homes
Visual identification is crucial when determining whether you have a cockroach or beetle problem. Here are some resources and tips to help you make the right call.
Resources for Accurate Identification
To aid in identification, consider:
- Online Guides: Websites dedicated to pest control often have photo galleries comparing different pests.
- Extension Services: Local university extension services can provide identification resources and may offer to examine a specimen.
- Pest Control Professionals: When in doubt, a trained professional can provide a definitive identification.
Tips for Homeowners
If you’re trying to determine whether you’re seeing a cockroach or a beetle in your home, keep these tips in mind:
- Observe the Behavior: Cockroaches are more likely to scurry away when exposed, while beetles might not react as quickly.
- Check the Time of Day: If you’re seeing the insect during the day, it’s more likely a beetle, as cockroaches are nocturnal.
- Inspect the Antennae: Cockroaches have long, thin antennae, whereas beetles’ antennae can be short, clubbed, or even feathery.
By using these identification strategies, you can better understand the nature of your pest problem and take the first steps toward control and prevention.
Evolutionary and Ecological Perspectives
Finally, considering the evolutionary history and ecological roles of these insects can provide a broader context for their presence in our environment.
Evolutionary History
Cockroaches are some of the oldest surviving insects on Earth, with a lineage that extends back over 300 million years. Their adaptability has allowed them to survive through countless environmental changes.
Beetles have an equally impressive evolutionary history, with fossil records dating back over 265 million years. Their success is due in part to their diverse adaptations, which have enabled them to occupy nearly every ecological niche.
Ecological Roles and Human Interaction
Cockroaches play a role in the decomposition of organic matter, which is a vital ecological process. However, their habit of invading human habitats has made them unwelcome pests.
Beetles serve many functions in the ecosystem, from pollinators to predators to decomposers. Their interaction with humans varies widely; some species are considered pests, while others are beneficial and even essential for controlling other insect populations.
Understanding these perspectives helps to appreciate the complexity of these insects beyond their role as household pests. It also underscores the importance of managing their populations in a way that respects their place in the ecosystem while protecting our homes and health.
Cockroach vs Bed Bug
Cockroaches and bed bugs, while both are household pests, exhibit different behaviors and physical characteristics. Bed bugs are small, wingless insects that feed exclusively on blood and are notorious for their bites, causing discomfort and irritation. They tend to hide in mattresses, bed frames, and furniture. Cockroaches, larger and with wings, have a varied diet and are known for their resilience and adaptability, thriving in various environments but commonly found in kitchens and bathrooms due to their preference for warmth and moisture.