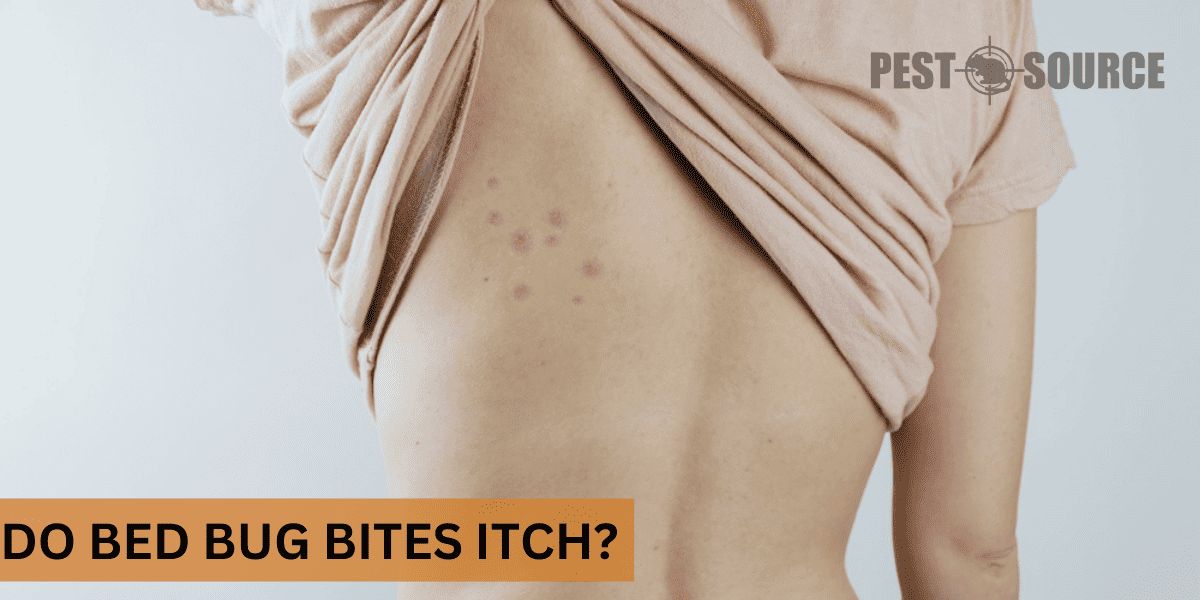
Bed bug bites often cause itching and discomfort due to the body’s allergic reaction to the bug’s saliva. The degree of itchiness can vary from person to person, ranging from mild to severe. Continue reading to learn more about the symptoms of bed bug bites and how to alleviate the itchiness they may cause.
POINTS
- Bed bug bites generally cause itching due to the body’s allergic reaction to the proteins in the bug’s saliva. However, the intensity of the itch varies by individual, depending on their immune response.
- Not all bed bug bites cause an itch. Some individuals may experience no symptoms, which does not necessarily mean the absence of an infestation.
- Persistent scratching of bed bug bites can lead to more severe skin issues, such as infection, hyperpigmentation, or scarring. Therefore, resisting the urge to scratch and giving bites adequate time to heal is crucial.
- Several methods can alleviate the discomfort of bed bug bites, from home remedies and over-the-counter treatments to prescribed medications. Applying cold compresses, creams, and certain essential oils can help soothe the itch.
- Despite varying reactions and symptoms to bed bug bites, the presence of the pests is most definitively indicated by visual signs, such as spots of blood on sheets or the sight of the bugs themselves. Immediate action via professional pest control services is advised upon detection.
The Concern of Bed Bug Bites
How do bed bugs bite?
Bed bugs, scientifically known as Cimex lectularius, have long, beak-like mouths that they use to pierce human skin. They use their elongated mouthparts to draw blood, which serves as their primary food source. They inject an anesthetic containing anticoagulant proteins into the skin to prevent blood clotting, allowing them to suck blood efficiently for up to 10 minutes.
How does the human body react to a bed bug bite?
Our bodies have a complex defensive system in place, and when bed bugs bite, they trigger an immune response. The body responds to the injected proteins by releasing histamines. This is an attempt to drive out foreign bodies, ending in inflammation and redness around the bite, commonly perceived as red, swollen bumps on the skin.
Do bed bug bites itch?
Yes, bed bug bites do itch. And the itch is not merely bothersome – it can be almost unbearable at times. The feeling of itchiness is a direct result of the body’s allergic reaction to the bug’s saliva. However, it’s important to remember that not everyone reacts the same way. Some people may not experience any discomfort, while for others, bed bug bites can cause severe itching.
Understanding the Itchiness of Bed Bug Bites
Why do bed bug bites itch?
It all comes down to the body’s reaction to foreign substances. The saliva injected by bed bugs contains several components that can stimulate the immune system, causing an allergic reaction resulting in itching. The body releases histamines to combat these foreign substances, leading to inflammation and the familiar itch.
Why do bed bug bites itch so badly?
The intensity of the itch is largely dependent on an individual’s immune response and can vary greatly from person to person. For some, the body releases a large amount of histamines, leading to more severe inflammation and stronger itchiness. If you’re among those with this intense response, remember: it’s merely your body making an effort to defend you against these unwelcome invaders.
Why do bed bug bites itch more at night?
It’s not so much that bed bug bites itch more at night, but rather that bed bugs are primarily nocturnal creatures. They feed most actively during the night, and as such, we often notice the itchiness upon waking up in the morning. Distractions during the day can also cause us to be less aware of the discomfort.
Variations in Itchiness and Individual Reactions to Bed Bug Bites
Do all bed bug bites itch?
No, not all bed bug bites itch. Just as some people are allergic to pollen or pet dander, some are allergic to the saliva of bed bugs and some are not. If you’re one of the individuals that do not have this allergy, the bed bug’s bite might not cause any noticeable symptoms.
Can bed bug bites not itch?
Yes, it is possible for bed bug bites not to itch. Some people have no reaction to bed bug bites, while others experience intense reaction causing more discomfort. People with no or mild allergic responses to the bed bug saliva might not experience any itchiness.
Why do some people experience severe itchiness while others do not?
The answer to this question lies in human biology. Everyone’s immune system works differently, and some people have immune systems that react more heavily to the allergens in bed bug saliva. These individuals experience severe itchiness due to a greater inflammation response.
Do bed bug bites itch immediately or is there a delay?
Typically, there’s a delay between the time of the bed bug bite and the onset of itching. The exact timing can vary depending on the individual’s immune response, but generally, the itchiness starts to set in a few hours after the bite and peaks within 24 to 48 hours.
Frequency and Duration of Itchiness from Bed Bug Bites
Do bed bug bites itch all the time?
Not necessarily. The itchiness of bed bug bites comes and goes in waves, usually peaking within a few days after the bite. You might not feel a newly formed bite as much, but the itch can intensify as hours go by.
Are bed bug bites always itchy?
No, bed bug bites are not always itchy. As we’ve discussed earlier, the itchiness largely depends on the individual’s sensitivity to the bed bug’s saliva. Some people experience strong itchiness, others feel a mild itch, and some have no itchiness at all.
When do bed bug bites start itching?
Generally, bed bugs bites start to itch a few hours after the initial bite. This is the body’s response to the foreign proteins introduced via the bed bug’s bite.
When do bed bug bites stop itching?
The itching from bed bug bites usually subsides within one to two weeks. This varies depending on the person and the severity of the reaction. If the itching persists beyond two weeks, it’s advisable to seek medical attention.
Methods to Alleviate Itching from Bed Bug Bites
How to stop bed bug bites from itching?
To relieve the discomfort caused by bed bug bites, there are a few methods you can use. First, never scratch the bite; while it may provide temporary relief, it can lead to infection or scarring. Try to clean the area with soap and water, and apply a cold compress to reduce swelling. Over-the-counter topicals like hydrocortisone cream or calamine lotion can bring relief to the itching.
What stops bed bug bites from itching?
Items you might have in your home, such as baking soda and water (creating a paste), apple cider vinegar, or lemon juice, can help alleviate the itch. Essential oils, such as peppermint or tea tree oil, can also provide some relief. Remember, though, that these are temporary solutions and should not replace proper medical treatment if symptoms persist or worsen.
How to prevent bed bug bites from itching?
Preventing bites from itching starts by preventing the bites entirely through pest control measures. Once bitten, the itch can be managed by applying over-the-counter creams, using cold compresses, and avoiding scratching the area.
Risks Associated with Itching and Scratching Bed Bug Bites
What are the dangers of scratching bed bug bites?
Scratching bed bug bites can lead to open sores and increase the risk of infection. The skin can become irritated and inflamed, which can cause secondary skin infections, such as impetigo, cellulitis, or even an abscess.
What can happen when you scratch bed bug bites?
Scratching can prolong the healing process. It can also result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, causing the skin around the bite to darken. Furthermore, in severe cases, continuous scratching can cause scarring.
Itchiness as a Symptom and Indicator of a Bed Bug Infestation
Do bed bugs always cause itching?
While it’s a common symptom, bed bugs do not always cause itching. Different people react differently to bed bug bites, and some may exhibit no symptoms at all. However, if you’re waking up with unexplained bites and spots on your body, it might indicate a bed bug problem, even if they don’t itch.
Can the absence of itchiness rule out a bed bug infestation?
No, the absence of itchiness doesn’t necessarily mean that there are no bed bugs. Some people have zero reaction to bed bug bites. If you suspect an infestation, it’s best to look for other signs such as spots of blood on your sheets, bed bug excrement, or even the bugs themselves.
Seeking Medical Attention
When should you see a doctor for bed bug bites itching?
While it’s normal to experience some amount of itching, if the itch is severe, continues for longer than a week, or is accompanied by signs of infection such as pus or increasing redness, it’s time to see a doctor. Also, if home remedies are ineffective at relieving your symptoms, a healthcare provider can offer stronger treatments.
What medical treatments are available for severe itching from bed bug bites?
Topical steroid creams or oral medications may be prescribed to manage severe itching. In the case of an infection, you may be given antibiotics. Antihistamines can also be of help to reduce allergic reactions. Always seek professional medical advice before starting any new medication.